Embarking on a journey to comprehend match the following descriptions with the correct aggregate supply curve, this exploration delves into the intricacies of this economic concept, unraveling its significance and applications with clarity and precision.
The aggregate supply curve, a fundamental tool in macroeconomic analysis, serves as a graphical representation of the relationship between the overall price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied within an economy. Understanding its dynamics and determinants is crucial for policymakers and economists seeking to navigate the complexities of economic fluctuations.
Overview of Aggregate Supply Curve: Match The Following Descriptions With The Correct Aggregate Supply Curve
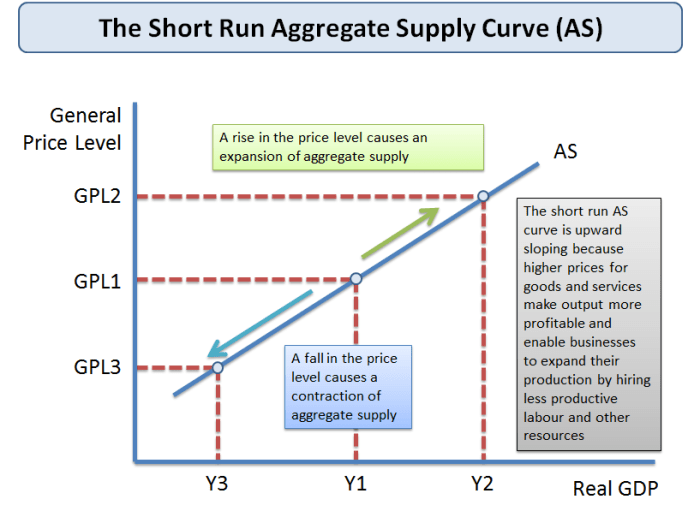
The aggregate supply curve (AS curve) is a graphical representation of the relationship between the overall price level in an economy and the quantity of goods and services supplied by producers at that price level. It shows the total amount of output that firms are willing and able to produce and sell at different price levels.
The aggregate supply curve is influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- The cost of production, such as wages, raw materials, and energy
- The availability of resources, such as labor, capital, and technology
- The expectations of producers about future economic conditions
Types of Aggregate Supply Curves
There are two main types of aggregate supply curves:
- Short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS): The SRAS curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of output supplied in the short run, when some factors of production are fixed.
- Long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS): The LRAS curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of output supplied in the long run, when all factors of production are variable.
The SRAS curve is typically upward sloping, while the LRAS curve is vertical.
Determinants of Aggregate Supply
The key determinants of aggregate supply include:
- Cost of production: An increase in the cost of production will lead to a decrease in aggregate supply, as producers are less willing to produce at a given price level.
- Availability of resources: An increase in the availability of resources will lead to an increase in aggregate supply, as producers are able to produce more at a given price level.
- Expectations of producers: If producers expect future economic conditions to be favorable, they are more likely to increase production, leading to an increase in aggregate supply.
Applications of Aggregate Supply Curve

The aggregate supply curve can be used to analyze a variety of economic issues, including:
- Inflation: The AS curve can be used to show how changes in the price level affect the quantity of output supplied.
- Economic growth: The AS curve can be used to show how changes in the determinants of aggregate supply affect the potential output of an economy.
- Government policies: The AS curve can be used to analyze the effects of government policies on the economy.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of the aggregate supply curve in economic analysis?
The aggregate supply curve plays a pivotal role in economic analysis as it provides insights into the overall productive capacity of an economy and its responsiveness to changes in the price level and other economic factors.
How can the aggregate supply curve be used to predict the effects of government policies?
By analyzing shifts in the aggregate supply curve, economists can assess the potential impact of government policies on the overall supply of goods and services, helping policymakers make informed decisions.